About IOS Training
iOS is the most used mobile OS in large corporations and iphones, Ipads are most popular mobile phones and tablets. If you search on naukri, monster or times job, you will see hundreds of jobs requiring 0 to 2 year experience for iOS app development. MNC's are looking for these skills but can't find enough MCAs and engineers who are trained in this.
IOS COURSE TRAINING HIGHLIGHTS
The application development process for iOSplatforms (iPod Touch, iPhone, iPad and future platforms) relies on a specialized paradigm of application development -the mobile paradigm. Designers and developers of mobile apps are challenged to provide superb user experience on resource-limited platforms where memory, processing power and battery life are at a premium.
In this course, we present Apple’s approach to mobile app design and development, as reflected in the design of the iOS platform, the Model – View-Controller (MVC) paradigm and iOS’s v various high and low-level frameworks. Objective-C, the native programming language for iOS, is exposed and explained step – by-step.
IOS TRAINING COURSE OUTCOME

WHO WILL BENEFIT
IOS TRAINING COURSE CURRICULUM
Part I. Language
 Compilation, Statements, and Comments
Compilation, Statements, and Comments
 Variable Declaration, Initialization, and Data Types
Variable Declaration, Initialization, and Data Types
 Structs
Structs
 Pointers
Pointers
 Arrays
Arrays
 Operators
Operators
 Flow Control and Conditions
Flow Control and Conditions
 Functions
Functions
 Pointer Parameters and the Address Operator
Pointer Parameters and the Address Operator
 Files
Files
 The Standard Library
The Standard Library
 More Preprocessor Directives
More Preprocessor Directives
 Data Type Qualifiers
Data Type Qualifiers
1. Just Enough C
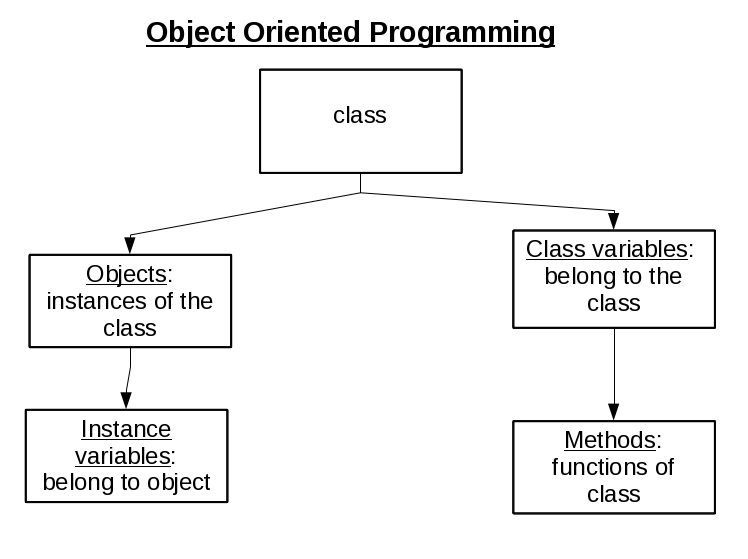
 Objects
Objects
 Messages and Methods
Messages and Methods
 Classes and Instances
Classes and Instances
 Class Methods
Class Methods
 Instance Variables
Instance Variables
 The Object-Based Philosophy
The Object-Based Philosophy
2. Object-Based Programming
3. Objective-C Objects and Messages
 An Object Reference Is a Pointer
An Object Reference Is a Pointer
 Instance References, Initialization, and nil
Instance References, Initialization, and nil
 Instance References and Assignment
Instance References and Assignment
 Instance References and Memory Management
Instance References and Memory Management
 Methods and Messages
Methods and Messages
 Calling a Method
Calling a Method
 Declaring a Method
Declaring a Method
 Nesting Method Calls
Nesting Method Calls
 No Overloading
No Overloading
 Parameter Lists
Parameter Lists
 When Message Sending Goes Wrong
When Message Sending Goes Wrong
 Messages to nil
Messages to nil
 Unrecognized Selectors
Unrecognized Selectors
 Typecasting and the id Type
Typecasting and the id Type
 Messages as Data Type
Messages as Data Type
 C Functions
C Functions
 CFTypeRefs
CFTypeRefs
 Blocks
Blocks
 Subclass and Superclass
Subclass and Superclass
 Interface and Implementation
Interface and Implementation
 Header File and Implementation File
Header File and Implementation File
 Class Methods
Class Methods
 The Secret Life of Classes
The Secret Life of Classes
4. Objective-C Classes
 How Instances Are Created
How Instances Are Created
 Ready-Made Instances
Ready-Made Instances
 Instantiation from Scratch
Instantiation from Scratch
 Nib-Based Instantiation
Nib-Based Instantiation
 Polymorphism
Polymorphism
 The Keyword self
The Keyword self
 The Keyword super
The Keyword super
 Instance Variables and Accessors
Instance Variables and Accessors
 Key–Value Coding
Key–Value Coding
 Properties
Properties
5. Objective-C Instances
Part II. IDE

6. Anatomy of an Xcode Project
 New Project
New Project
 The Project Window
The Project Window
 The Navigator Pane
The Navigator Pane
 The Utilities Pane
The Utilities Pane
 The Editor
The Editor
 The Project File and Its Dependents
The Project File and Its Dependents
 The Target
The Target
 Build Phases
Build Phases
 Build Settings
Build Settings
 Configurations
Configurations
 Schemes and Destinations
Schemes and Destinations
 Renaming Parts of a Project
Renaming Parts of a Project
 From Project to Running App
From Project to Running App
 Build Settings
Build Settings
 Property List Settings
Property List Settings
 Nib Files
Nib Files
 Additional Resources
Additional Resources
 Code and the App Launch Process
Code and the App Launch Process
 Frameworks and SDKs
Frameworks and SDKs
 A Tour of the Nib Editor Interface
A Tour of the Nib Editor Interface
 The Document Outline
The Document Outline
 Canvas
Canvas
 Inspectors and Libraries
Inspectors and Libraries
 Nib Loading
Nib Loading
 Outlets and the Nib Owner
Outlets and the Nib Owner
 Creating an Outlet
Creating an Outlet
7. Nib Management
 Misconfiguring an Outlet
Misconfiguring an Outlet
 Deleting an Outlet
Deleting an Outlet
 More Ways to Create Outlets
More Ways to Create Outlets
 Outlet Collections
Outlet Collections
 Action Connections
Action Connections
 Table
Table
 Additional Initialization of Nib-Based Instances
Additional Initialization of Nib-Based Instances
8. Documentation
 The Documentation Window
The Documentation Window
 Class Documentation Pages
Class Documentation Pages
 Sample Code
Sample Code
 Other Resources
Other Resources
 Quick Help
Quick Help
 Symbols
Symbols
 Header Files
Header Files
 Internet Resources
Internet Resources
9. Life Cycle of a Project
 Device Architecture and Conditional Code
Device Architecture and Conditional Code
 Version Control
Version Control
 Editing Your Code
Editing Your Code
 Auto completion
Auto completion
 Snippets
Snippets
 Fix-it and Live Syntax Checking
Fix-it and Live Syntax Checking
 Navigating Your Code
Navigating Your Code
 Running in the Simulator
Running in the Simulator
 Debugging
Debugging
 Caveman Debugging
Caveman Debugging
 The Xcode Debugger
The Xcode Debugger
 Unit Testing
Unit Testing
 Static Analyzer
Static Analyzer
 Clean
Clean
 Running on a Device
Running on a Device
 Obtaining a Certificate
Obtaining a Certificate
 Obtaining a Development Provisioning Profile
Obtaining a Development Provisioning Profile
 Running the App
Running the App
 Profile and Device Management
Profile and Device Management
 Gauges and Instruments
Gauges and Instruments
 Localization
Localization
 Archiving and Distribution
Archiving and Distribution
 Ad Hoc Distribution
Ad Hoc Distribution
 Final App Preparations
Final App Preparations
 Icons in the App
Icons in the App
 Other Icons
Other Icons
 Launch Images
Launch Images
 Screenshots
Screenshots
 Property List Settings
Property List Settings
 Submission to the App Store
Submission to the App Store
Part III. Cocoa
10. Cocoa Classes
 Subclassing
Subclassing
 Categories 268
Categories 268
 Splitting a Class
Splitting a Class
 Class Extensions
Class Extensions
 Protocols
Protocols
 Informal Protocols
Informal Protocols
 Optional Methods
Optional Methods
 Some Foundation Classes
Some Foundation Classes
 Useful Structs and Constants
Useful Structs and Constants
 NSString and Friends
NSString and Friends
 NSDate and Friends
NSDate and Friends
 NSNumber
NSNumber
 NSValue
NSValue
 NSData
NSData
 Equality and Comparison
Equality and Comparison
 NSIndexSet
NSIndexSet
 NSArray and NSMutableArray
NSArray and NSMutableArray
 NSSet and Friends
NSSet and Friends
 NSDictionary and NSMutableDictionary
NSDictionary and NSMutableDictionary
 NSNull
NSNull
 Immutable and Mutable
Immutable and Mutable
 Property Lists
Property Lists
 The Secret Life of NSObject
The Secret Life of NSObject
11. Cocoa Events
 Reasons for Events
Reasons for Events
 Subclassing
Subclassing
 Notifications
Notifications
 Receiving a Notification
Receiving a Notification
 Unregistering
Unregistering
 Posting a Notification
Posting a Notification
 NSTimer 305Delegation
NSTimer 305Delegation
 Cocoa Delegation
Cocoa Delegation
 Implementing Delegation
Implementing Delegation
 Data Sources
Data Sources
 Actions
Actions
 The Responder Chain
The Responder Chain
 Deferring Responsibility
Deferring Responsibility
 Nil-Targeted Actions
Nil-Targeted Actions
 Swamped by Events
Swamped by Events
 Delayed Performance
Delayed Performance

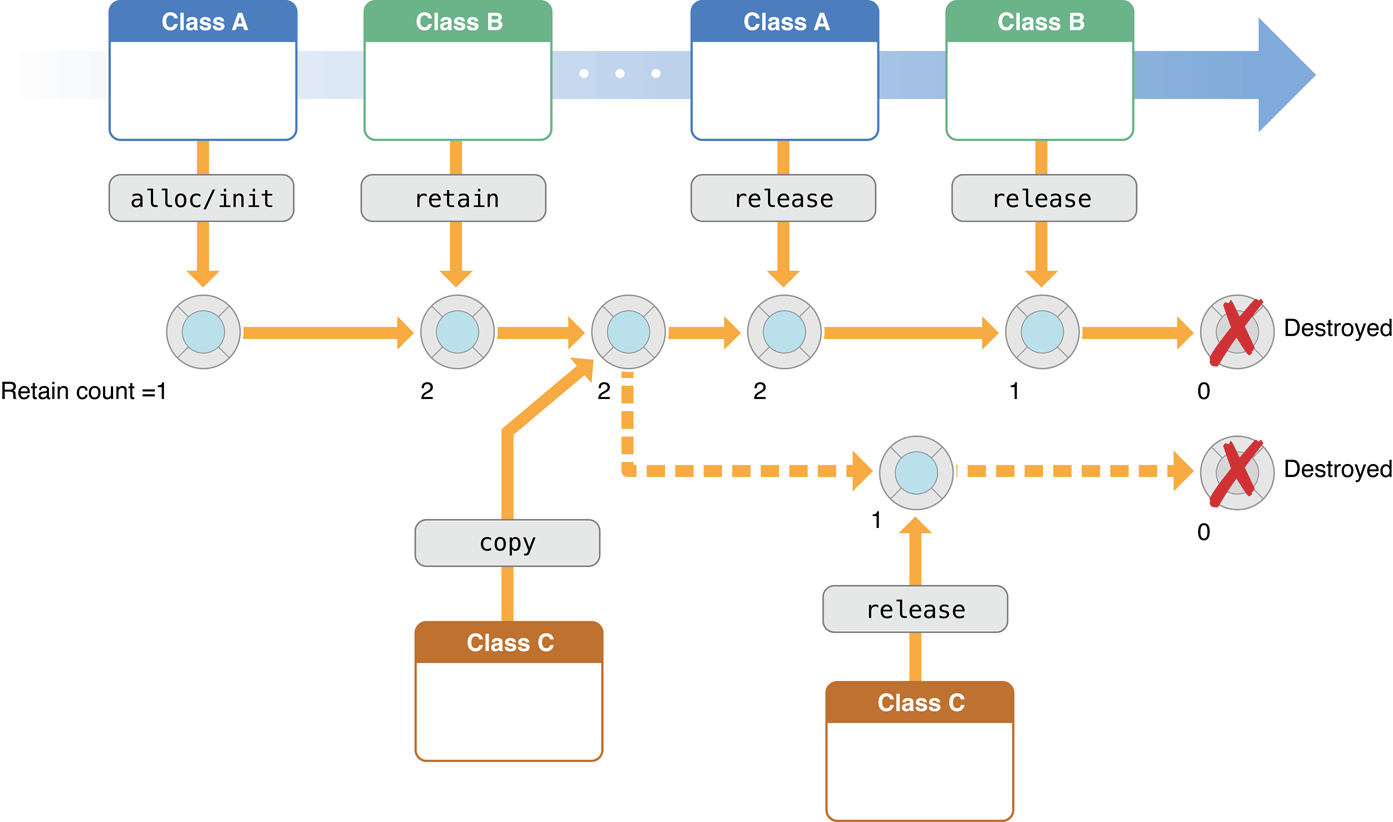
12. Accessors and Memory Management
 Accessors
Accessors
 Key–Value Coding
Key–Value Coding
 KVC and Outlets
KVC and Outlets
 Key Paths
Key Paths
 Array Accessors
Array Accessors
 Memory Management
Memory Management
 Principles of Cocoa Memory Management
Principles of Cocoa Memory Management
 The Rules of Cocoa Manual Memory Management
The Rules of Cocoa Manual Memory Management
 What ARC Is and What It Does
What ARC Is and What It Does
 How Cocoa Objects Manage Memory
How Cocoa Objects Manage Memory
 Autorelease
Autorelease
 Memory Management of Instance Variables (Non-ARC)
Memory Management of Instance Variables (Non-ARC)
 Memory Management of Instance Variables (ARC)
Memory Management of Instance Variables (ARC)
 Retain Cycles and Weak References
Retain Cycles and Weak References
 Unusual Memory Management Situations
Unusual Memory Management Situations
 Nib Loading and Memory Management
Nib Loading and Memory Management
 Memory Management of Global Variables
Memory Management of Global Variables
 Memory Management of CFTypeRefs
Memory Management of CFTypeRefs
 Memory Management of Pointer-to-Void Context Info
Memory Management of Pointer-to-Void Context Info
 Properties
Properties
 Property Memory Management Policies
Property Memory Management Policies
 Property Declaration Syntax
Property Declaration Syntax
 Property Accessor Synthesis
Property Accessor Synthesis
 Dynamic Accessors
Dynamic Accessors
13. Communication Between Objects
 Visibility by Instantiation
Visibility by Instantiation
 Visibility by Relationship
Visibility by Relationship
 Global Visibility
Global Visibility
 Notifications
Notifications
 Key–Value Observing
Key–Value Observing